- by OfficialHOVSCO
Why Understanding Ebike Classes and Their Legal Status Matters for Riders
- by OfficialHOVSCO
Ebike classes categorize electric bikes based on their motor assistance, speed limits, and throttle use, directly influencing where and how you can legally ride them. Knowing these classes helps riders comply with laws, choose the right bike for their needs, and safely navigate public roads, trails, and bike paths.
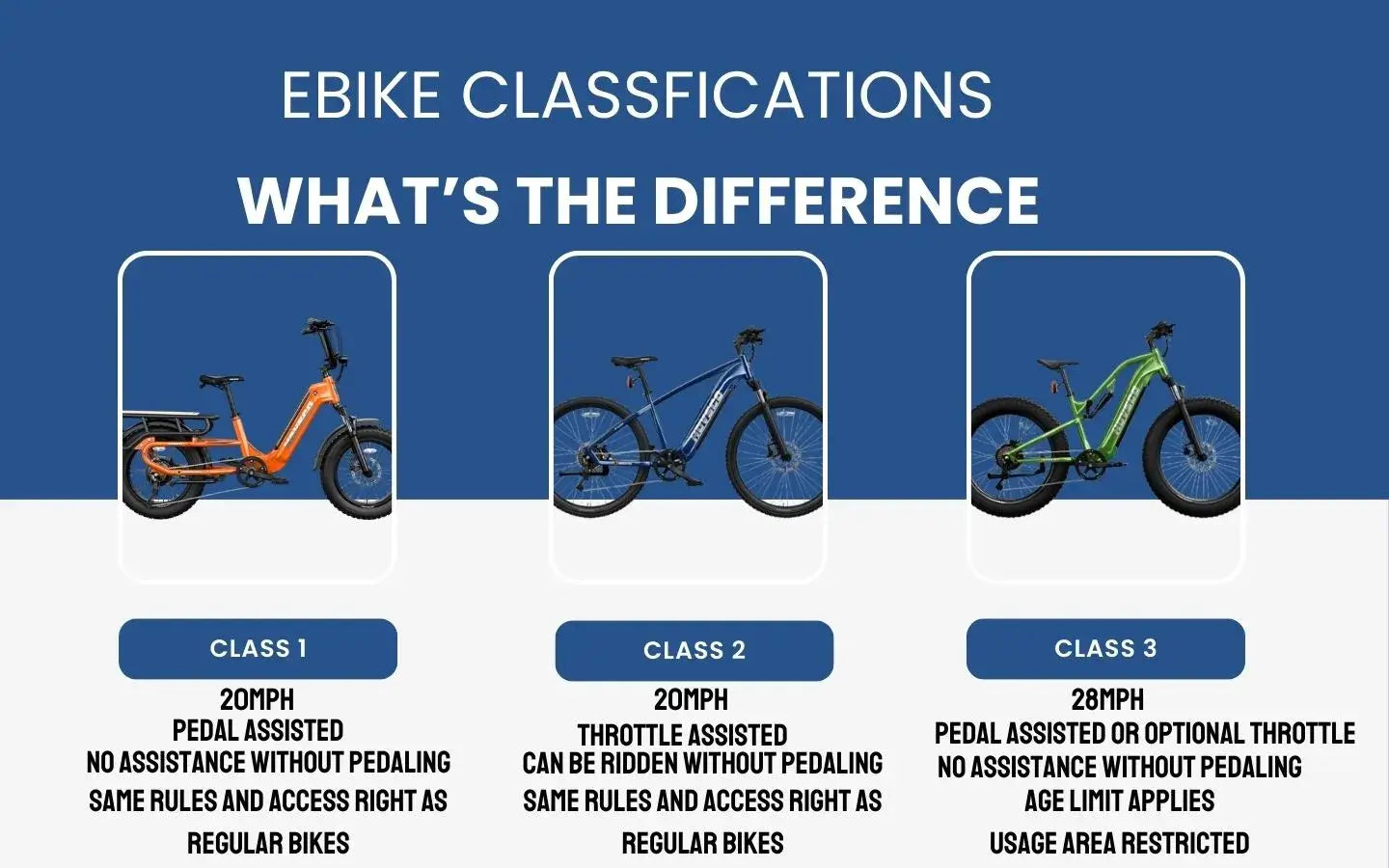
E-bikes fall into three classes: Class 1 (pedal-assist only, max 20 mph), Class 2 (throttle and pedal-assist, max 20 mph), and Class 3 (pedal-assist only, max 28 mph). Legal access varies by class.
Ebike classes are primarily divided into three categories based on motor assistance type, maximum assisted speed, and throttle availability:
These classifications help regulate usage and safety, distinguishing ebikes from mopeds or motorcycles.
Class 1 and 3 e-bikes use pedal assist only, while Class 2 adds a throttle. Class 3 offers higher speeds, making it ideal for commuting, whereas Class 1 is more widely accepted on trails.
Pedal Assist Systems (PAS) sense when and how much assistance to provide. There are two main types:
Most modern Class 1 and Class 3 ebikes use torque sensing for efficient power delivery and better battery range, while some Class 2 ebikes may use cadence sensing.
Class 3 bikes often face age and helmet laws and may be banned from certain bike paths. Class 1 and 2 have broader access but may be restricted in nature preserves or on sidewalks.
Legal restrictions vary by class and jurisdiction:
Understanding these legal distinctions is crucial for compliance and safety.
Chart: Ebike Classes and Their Legal Access
| Class | Max Assisted Speed | Throttle Allowed | Common Legal Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | 20 mph | No | Bike paths, multi-use trails, roads |
| Class 2 | 20 mph | Yes | Roads; often restricted on trails |
| Class 3 | 28 mph | Sometimes (20 mph limit) | Roads only; banned on most trails |
Throttle use allows riders to propel the bike without pedaling, which changes how ebikes are regulated. Class 2 ebikes, equipped with throttles, are often subject to stricter rules and may be prohibited on trails reserved for pedal-assist bikes. Throttle-enabled ebikes blur the line between bicycles and motorized vehicles, affecting where they can be legally ridden and sometimes requiring additional licensing or registration.
Speed limits for each class are designed to balance rider safety with traffic flow. Class 1 and 2 ebikes max out at 20 mph to ensure compatibility with traditional bicycles on shared paths. Class 3 ebikes can reach 28 mph, making them suitable for faster commuting but raising safety concerns on mixed-use trails, leading to legal restrictions. Higher speeds require riders to exercise greater caution and often necessitate additional safety gear and awareness.
Class 1 is best for recreational trails, Class 2 suits urban errands with throttle convenience, and Class 3 excels in long-distance commuting. Choose based on terrain, speed, and access rules.
Choosing the right class depends on your riding style, terrain, and legal access.
A Class 1 ebike is a pedal-assist electric bike that provides motor assistance only when you pedal, with no throttle. It assists up to 20 mph, making pedaling easier on hills and long rides while maintaining a natural cycling feel. This design balances exercise with electric boost for versatile, accessible riding.
E-bike classes include:
Each class differs by motor assistance type and maximum speed.
Ebike classes determine where and how you can ride. Class 1 bikes are allowed on most bike paths and trails where regular bikes are permitted. Class 2 and 3 may face more restrictions due to throttle use or higher speeds. Local laws vary, so knowing your e-bike class helps ensure legal and safe riding.
Ebike classes play a crucial role in determining where and how you can ride your electric bike, as they are defined by the type of motor assistance and maximum speed limits. Class 1 e-bikes provide pedal-assist only, with motor support up to 20 mph, and are generally allowed on most bike paths, multi-use trails, and roads where traditional bikes are permitted. Class 2 e-bikes include both pedal-assist and throttle operation, also capped at 20 mph, and usually share similar access privileges as Class 1 but may face some restrictions due to throttle use. Class 3 e-bikes offer pedal-assist up to 28 mph but no throttle, often restricted to roads and bike lanes, and may require riders to wear helmets and meet age limits.
Local laws vary widely, so understanding your e-bike’s class helps ensure you ride legally and safely. Many states have adopted this three-class system, but regulations on helmet use, minimum rider age, and allowed riding locations differ. For example, Class 3 e-bikes are often excluded from multi-use trails and may be subject to stricter rules. Knowing your e-bike’s class and corresponding regulations helps avoid fines and promotes responsible riding, ensuring you enjoy your ride while respecting local laws and safety standards.
When purchasing an ebike, consider your typical riding environment and legal regulations. Class 1 ebikes offer broad trail access and natural pedal-assist, making them versatile for most riders. Class 2 ebikes provide throttle convenience but may face usage restrictions, so check local laws before buying. Class 3 ebikes deliver higher speeds for commuting but are limited on trails and require careful handling. Always verify that the ebike complies with your region’s legal classification and safety standards. HOVSCO’s commitment to innovation ensures a range of ebikes tailored to diverse needs, combining performance with compliance.
“HOVSCO understands that navigating ebike classes and their legal statuses is essential for riders to enjoy safe, lawful, and efficient cycling experiences. Our designs prioritize compliance with regulations while delivering powerful, user-friendly electric bikes. We encourage riders to choose the class that fits their lifestyle and local laws, ensuring every ride is both exhilarating and responsible.”
What distinguishes Class 1, 2, and 3 ebikes?
Class 1 offers pedal-assist up to 20 mph with no throttle; Class 2 adds a throttle up to 20 mph; Class 3 provides pedal-assist up to 28 mph, sometimes with a limited throttle.
Can I ride a Class 2 ebike on all bike paths?
No, many trails and bike paths restrict Class 2 ebikes due to their throttle capability, often limiting them to roads.
Do I need a license to ride a Class 3 ebike?
Generally, no license is required, but local laws vary, especially since Class 3 ebikes can reach higher speeds.
How does pedal assist differ from throttle?
Pedal assist requires pedaling to activate the motor, while throttle allows motor power without pedaling.
Are all ebikes legal everywhere?
No, ebike legality depends on class and local regulations; always check your area’s laws before riding.
Understanding Ebike Classes and Their Legal Status
Electric bikes, or ebikes, have revolutionized the way we commute, exercise, and explore the outdoors. Their versatility and eco-friendliness have made them increasingly popular across the globe, including in the U.S. However, as their popularity grows, so does the need for clarity about their classifications and legal status. This comprehensive guide will delve into the different ebike classes and answer the pressing question: Are ebikes street legal?
Ebikes are typically categorized into three distinct classes. Each class is defined based on the bike’s features, specifically its power-assist mechanisms and speed capabilities. Let’s break them down:
| Ebike Class | Pedal Assist | Throttle Assist | Max Assisted Speed | Typical Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Yes | No | 20 mph | Bike paths, trails |
| Class 2 | Optional | Yes | 20 mph | Urban riding |
| Class 3 | Yes | No | 28 mph | Commuting, roads |
Class 1 ebikes provide assistance only when the rider is pedaling. This assistance is capped at a maximum speed of 20 mph. These bikes are ideal for beginners or those seeking a more traditional biking experience with an added boost.
Key Features:
Class 2 ebikes feature a throttle that allows the bike to propel itself without the rider pedaling. Like Class 1, their maximum speed is capped at 20 mph. These bikes are perfect for riders who want the option of a fully electric ride.
Key Features:
Class 3 ebikes provide pedal assistance up to a higher speed limit of 28 mph. They are equipped with a speedometer and are designed for more experienced riders or those using the ebike for commuting.
Key Features:
Yes, e-bikes are generally street legal in the U.S., but regulations vary by state. Class 1 and 2 e-bikes are typically allowed on bike paths and multi-use trails, while Class 3 e-bikes are often restricted to roadways and bike lanes. Always check local laws to ensure compliance.
The legality of riding an ebike on public roads and paths depends on its classification and the local regulations of the state or city. In the United States, most states have adopted a three-class system to regulate ebike usage. Here are the general rules:
At the federal level, ebikes are defined as bicycles as long as their motors are under 750 watts (1 horsepower) and they do not exceed 20 mph under motor power alone. This definition exempts them from being classified as motor vehicles, thus avoiding the need for licensing, registration, or insurance.
States have the authority to set specific rules for ebike usage. While many states align with the three-class system, variations exist. Let’s explore some common regulations:
| Regulation Aspect | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Helmet Required | No (under a certain age) | No (under a certain age) | Yes (for all riders) |
| Age Restriction | None | None | 16+ years |
| Path Access | Allowed | Restricted in some areas | Limited to roads, bike lanes |
Helmet Requirements:
Age Restrictions:
Where You Can Ride:
To ride legally and safely, always wear a helmet, adhere to traffic laws, and use appropriate lighting and reflectors. Ensure your e-bike matches the class permitted in your area and avoid unauthorized modifications that could alter its classification. Regular maintenance is also crucial for safety.
Before hitting the road, familiarize yourself with the specific ebike regulations in your area. Websites like PeopleForBikes and local government portals are excellent resources for updated information.
Investing in safety gear is crucial, especially for Class 3 ebikes. Key items include:
While ebikes don’t require insurance, having liability coverage through your homeowner’s or renter’s insurance can offer peace of mind.
Hovsco e-bikes offer high-quality components like Samsung/LG batteries and powerful motors, providing reliable performance. Features such as torque sensors, integrated lighting, and sleek designs enhance the riding experience. With models catering to various needs, Hovsco combines functionality with style.
At Hovsco, we design ebikes that meet diverse needs while complying with legal standards. Whether you’re looking for a reliable commuter bike or an adventure-ready ebike, our products adhere to U.S. regulations and prioritize rider safety.
| Hovsco Model | Class | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| HovRanger | Class 1 | Pedal-assist up to 20 mph, lightweight frame |
| HovAlpha | Class 2 | Throttle assist, powerful motor for urban flexibility |
| HovBeta | Class 3 | High-speed pedal assist up to 28 mph, built-in speedometer |
Our team is here to assist you in selecting the right ebike and understanding the laws in your region. We also provide resources for maintenance and safety tips to enhance your riding experience.
Ebikes are transforming transportation, offering a sustainable and enjoyable alternative to traditional vehicles. Understanding ebike classes and their legalities ensures you can ride confidently and responsibly. At Hovsco, we’re committed to empowering riders with high-quality ebikes that cater to various lifestyles while staying compliant with regulations.
Explore our range of ebikes and find the perfect ride for your journey. For more information, visit our ebike FAQ page or contact our support team today.
Share:
Which Colorado E-Bike Rebates and Tax Credits Can Save You Money?
How to Turn Your Regular Bike into an E-Bike with a Conversion Kit